Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is a versatile compound that plays a crucial role in a wide range of industries, from pharmaceuticals and cosmetics to food and industrial applications. Whether you're new to the world of chemistry or exploring the manufacturing side of this compound, understanding how polyethylene glycol is made can offer valuable insights into its importance. This article will explore PEG's composition, production process, purification methods, and its diverse applications.
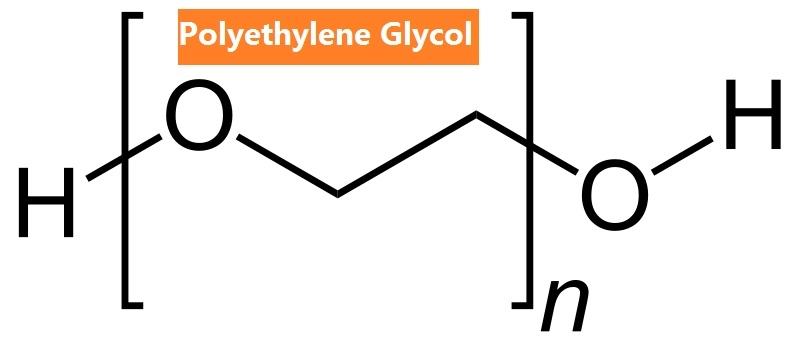
Polyethylene glycol is a synthetic polymer, a product of the reaction between ethylene oxide and water or other ethylene oxide derivatives. PEG is widely used because of its ability to dissolve in both water and organic solvents, as well as its low toxicity. Its molecular structure consists of repeating units of ethylene glycol, making it a part of a broader family of compounds known as polyethers. It can vary in molecular weight, and depending on its size, it can range from a liquid to a solid.
In its various forms, PEG can serve multiple purposes: it’s used in laxatives, as a stabilizer in cosmetic products, and even in industrial applications such as lubricants and anti-freeze.
The production of polyethylene glycol begins with two primary raw materials: ethylene oxide and water. Ethylene oxide, a reactive and highly versatile compound, is the building block that starts the polymerization process. It's usually obtained from petroleum products and reacts with water or other polyols (compounds containing multiple hydroxyl groups) to form PEG.
The choice of raw materials plays a critical role in determining the final properties of PEG. For instance, the molecular weight of PEG can be adjusted by altering the ratio of ethylene oxide to water, which influences its viscosity and solubility. In addition, using different initiators can result in PEG with varied applications, ranging from medical formulations to industrial lubricants.
The process of making polyethylene glycol involves a polymerization reaction where ethylene oxide is added to water. This reaction typically occurs in a closed reactor under controlled temperatures and pressures to ensure safety and efficiency. Ethylene oxide is a highly reactive compound, so its handling requires careful attention to avoid unwanted reactions.
Once ethylene oxide and water are mixed, they undergo a process known as ring-opening polymerization. During this process, the ethylene oxide molecules open up their ring structure and connect to form long chains of polyethylene glycol. This reaction continues until the desired molecular weight is achieved.
One of the defining features of PEG manufacturing is the ability to control the molecular weight of the polymer. By adjusting the amount of ethylene oxide and the reaction conditions, manufacturers can produce PEGs of varying lengths. The resulting PEG can be a liquid, solid, or semi-solid, depending on its molecular size. For instance, PEG 400 is a liquid, while PEG 8000 is a solid wax-like substance.
After polymerization, the raw PEG undergoes a purification process to remove any residual impurities. This is a critical step in ensuring that the final product meets the required standards, especially in industries like pharmaceuticals and cosmetics, where purity is paramount.
One common method for purifying PEG is through distillation, where excess ethylene oxide, water, and other by-products are removed. This step ensures that only pure PEG remains. In some cases, PEG may also undergo filtration or crystallization to further refine its quality.
Purification is essential because impurities can affect the performance of PEG in its intended applications. For example, residual chemicals might lead to skin irritation in cosmetic products or interfere with the efficacy of pharmaceutical formulations. As such, the purification process must be precisely controlled to meet industry standards.

Polyethylene glycol’s versatility makes it a popular choice across various industries. Below are some of the most notable applications: